Cryotherapy is also known as as cold therapy, this novel treatment has gained considerable popularity in the wellness and medical sectors. By exposing the body to extremely low temperatures, cryotherapy improves physical recovery, stimulates healing, and even helps mental health. Originally used by sportsmen for pain treatment and muscle recovery, cryotherapy today finds numerous medical and cosmetic uses. The multiple applications, the technique itself, the hazards involved, and the advantages that make cryotherapy a preferred treatment for many will be covered in this thorough discussion.
What is Cryotherapy ?
Cryotherapy is a treatment that involves exposing the body to extremely cold temperatures for a short period. Mostly, there are two forms of cryotherapy:
Whole-Body Cryotherapy (WBC)
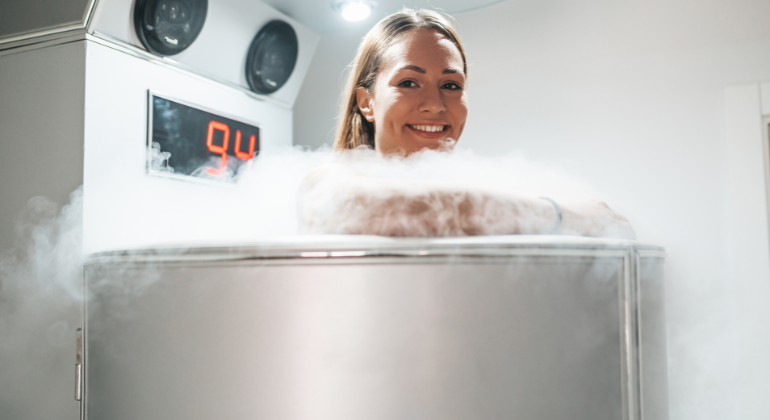
Whole-body cryotherapy (WBC) submerges the complete body in a cryotherapy chamber or cryosauna. Lowering temperatures down to as low as – 130°C, Usually spanning two to four minutes, this treatments give a whole-body sensation.
Localized Cryotherapy
Localized cryotherapy applies extreme cold to the affected area. Using cooling chemical or liquid nitrogen applicators on targeted areas—such as joints, muscles, or skin lesions
Popular Uses of Cryotherapy
One flexible treatment with great range of application is cryotherapy. These are some of the most often utilized and popular programs on demand.
1. Pain Relief and Muscle Recovery
Cryotherapy helps particularly those athletes who want to speed up recovery following demanding exercises and minimize muscular soreness. For diseases like tendinitis and arthritis, this treatment is quite successful since the cold helps to reduce inflammation, the main cause of discomfort. Cold treatment becomes vitally necessary for athletes nowadays to maintain best performance and ensure speedier recovery.
2. Cosmetic Purposes
Cryotherapy is also used for cosmetic purposes, such as reducing the appearance of cellulite or tightening the skin. The cold temperatures can cause vasoconstriction, temporarily tightening blood vessels, skin tightening and increased collagen production of surrounding tissues.
3. Weight Loss and Metabolism Boost
For weight loss, cryotherapy is starting to becoming somewhat well known. The idea behind it is that while the body works harder to keep its core temperature, cold can raise metabolism, therefore increasing calorie burn. Practitioners target and kill fat cells using cryolipolysis (cool sculpting) , often known as fat freezing, therefore enhancing other weight loss procedures with a cold treatment metabolic boost.
4. Mental Health Benefits and improved sleep –
Recent studies highlight potential advantages for mental health from cryotherapy. From cryotherapy for anxiety treatment to cold therapy for depression, lowering anxiety and depression symptoms has shown promise. Extreme cold generates endorphins, thereby improving mood, mental clarity, and key whole-body cryotherapy advantages for emotional well-being.
Cryotherapy has been reported to improve sleep quality in some individuals. The relaxation and reduction in muscle tension post-treatment may help promote better sleep, which is crucial for mental health.
5. Enhanced Healing
Some studies suggest that localised cryotherapy can stimulate blood flow and promote the body’s natural healing processes. This may result in faster tissue repair and improved recovery from injuries.
What to Expect During a Cryotherapy Session
Knowing what to expect helps to calm and reassure the experience. Here we break out the common cryotherapy techniques:
Whole-Body Cryotherapy (WBC) Procedure
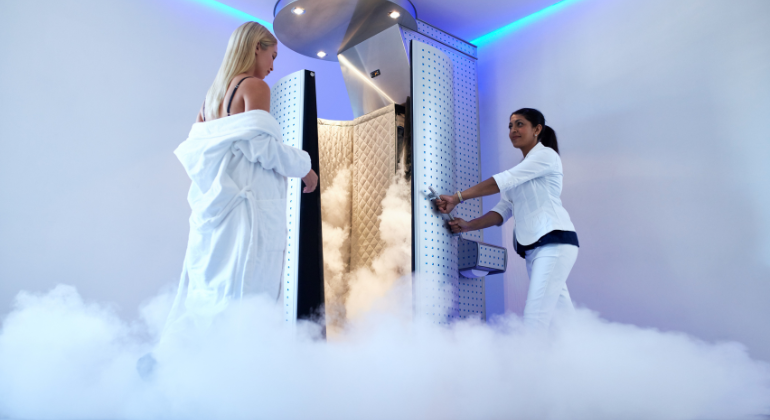

Under a whole-body cryotherapy treatment, the patient swiftly lowers the temperature by entering a cryosauna or chamber filled with nitrogen-cooled air. Usually running two to four minutes, every session closely supervised to ensure patient safety. Among the protective equipment used to prevent frostbite and enhance the full cryosauna experience are gloves, stockings, and sometimes a mask.
Localized Cryotherapy Procedure
Localized cryotherapy—a joint, muscle, a skin lesion—is applying cold straight to the specific area being treated. Liquid nitrogen or another cooling chemical delivers the cold; the time of treatment depends on the ailment.
It delivers a steady stream of Carbon Dioxide gas at particular temperature. The freezing gas is delivered at a pressure , instantly removing heat and inflammation. Within 30 seconds surface skin temperature is reduced to 4°C. The body reacts by immediately dilating blood vessels and increasing the flow of blood and oxygen to the affected area. By reducing inflammation and increasing blood flow, the body speeds up the recovery process, eliminates pain and relaxes muscles in the effected area.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Cryotherapy
Though most people consider cryotherapy to be safe, it is good to be informed of the potential risks and side effects:
1. Frostbite
Frostbite is a major worry in whole-body cryotherapy. Depending on the skin type, extreme cold for too long or inappropriate use of protective gear might also lead to this. Among symptoms are numbness, redness, and in severe cases tissue damage. One should be aware of cryotherapy frostbite’s possibility.
2. Nerve Damage
In localized cryotherapy, there is a risk of nerve damage, especially if the cold is applied too intensely or for an extended period. This highlights the importance of having treatments performed by experienced professionals to minimize the cryotherapy nerve damage risk.
3. Skin Irritation and Burns
Skin irritation, blistering, or even burns can occur, particularly with localized treatments using liquid nitrogen.
4. Contraindications
Cryotherapy isn’t suitable for everyone. Individuals with conditions like Raynaud’s disease, severe hypertension, or cold allergies should avoid this treatment. Pregnant women and those with cardiovascular conditions are also advised against undergoing cryotherapy.
Benefits of Cryotherapy?
Despite the risks, cryotherapy offers a multitude of benefits that have contributed to its growing popularity:
1. Reduction of Inflammation
Cryotherapy is effective at reducing inflammation, which is often the root cause of chronic pain conditions such as arthritis and fibromyalgia. By minimizing inflammation, cryotherapy supports faster recovery and lowers the risk of injury.
2. Enhanced Blood Circulation
Alternating between cold exposure and rewarming can significantly improve blood circulation, promoting better oxygen and nutrient delivery throughout the body and aiding in detoxification.
3. Mood Improvement and Stress Relief
The extreme cold triggers the release of endorphins, leading to improved mood, reduced stress, and a decrease in anxiety and depression symptoms.
4. Skin Health and Anti-Aging:
Cryotherapy can stimulate collagen production, reducing signs of aging and improving overall skin health. It is often used in cosmetic treatments to minimize fine lines, wrinkles, and skin discoloration.
5. Potential for Weight Loss
While not a standalone solution, cryotherapy can be a valuable complement to other weight loss strategies by boosting metabolism and helping with fat reduction through techniques like cryolipolysis.
Conclusion
Cryotherapy is a versatile and innovative treatment that offers a range of benefits, from pain relief and muscle recovery to improved mental health and enhanced skin care. However, like any medical treatment, it carries certain risks, and it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if it’s the right option for you.
Whether you’re an athlete looking to recover faster, someone managing chronic pain, or simply curious about the potential benefits of cold therapy, cryotherapy is worth considering under the guidance of a professional.
For more information and to schedule a consultation, visit Painflame clinic .
Recent Blog : Pros and Cons of Home Physiotherapy
What is Cryotherapy and How Does It Work?
Cryotherapy is a treatment that involves exposing the body to extremely cold temperatures for a short period, usually using liquid nitrogen or cold air. There are two main types: Whole-Body Cryotherapy (WBC), which immerses the entire body in a chamber cooled to temperatures as low as -130°C, and Localized Cryotherapy, which targets specific areas like joints, muscles, or skin lesions. The extreme cold helps reduce inflammation, boost blood circulation, and promote healing.
Is Cryotherapy Safe, and What Are the Risks?
Cryotherapy is generally considered safe when performed by trained professionals, but there are some risks to be aware of. Potential side effects include frostbite, nerve damage, and skin irritation or burns, particularly in localized treatments. Additionally, cryotherapy is not recommended for individuals with certain conditions like Raynaud’s disease, severe hypertension, or cold allergies, and it should be avoided during pregnancy.
What Are the Benefits of Cryotherapy for Athletes?
Athletes often use cryotherapy to speed up recovery after intense workouts and reduce muscle soreness. The cold temperatures help lower inflammation, which is a major cause of pain and discomfort. By minimizing inflammation, cryotherapy supports faster recovery, allowing athletes to maintain peak performance. It’s also beneficial for treating sports-related conditions like tendinitis and arthritis.
Can Cryotherapy Help with Weight Loss?
Cryotherapy is gaining popularity as a supplementary method for weight loss. The idea is that exposure to extreme cold increases the body’s metabolism as it works to maintain its core temperature. This can lead to more calories being burned. Techniques like cryolipolysis, also known as fat freezing, can target and kill fat cells, enhancing the effects of other weight loss strategies.
How Does Cryotherapy Improve Skin Health?
Cryotherapy can benefit skin health by stimulating collagen production, which helps reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and skin discoloration. The cold temperatures cause vasoconstriction, tightening blood vessels and improving skin tone. As a result, cryotherapy is often used in cosmetic treatments to promote a more youthful and vibrant appearance.